How To Run A Python Script In Windows Terminal
Getting Started with Python in VS Lawmaking
In this tutorial, y'all use Python 3 to create the simplest Python "Hello World" application in Visual Studio Code. By using the Python extension, you make VS Code into a great lightweight Python IDE (which you may notice a productive alternative to PyCharm).
This tutorial introduces you to VS Lawmaking every bit a Python environs, primarily how to edit, run, and debug code through the following tasks:
- Write, run, and debug a Python "How-do-you-do World" Awarding
- Learn how to install packages by creating Python virtual environments
- Write a simple Python script to plot figures inside VS Code
This tutorial is not intended to teach you Python itself. Once you are familiar with the basics of VS Code, you tin can then follow any of the programming tutorials on python.org inside the context of VS Code for an introduction to the language.
If you lot have whatsoever problems, feel free to file an effect for this tutorial in the VS Code documentation repository.
Prerequisites
To successfully complete this tutorial, you demand to get-go setup your Python evolution surroundings. Specifically, this tutorial requires:
- VS Code
- VS Code Python extension
- Python three
Install Visual Studio Code and the Python Extension
-
If y'all have not already done so, install VS Code.
-
Side by side, install the Python extension for VS Lawmaking from the Visual Studio Marketplace. For additional details on installing extensions, see Extension Market place. The Python extension is named Python and it'due south published past Microsoft.
Install a Python interpreter
Along with the Python extension, you need to install a Python interpreter. Which interpreter y'all employ is dependent on your specific needs, but some guidance is provided below.
Windows
Install Python from python.org. You lot can typically use the Download Python button that appears get-go on the page to download the latest version.
Note: If yous don't have admin access, an additional option for installing Python on Windows is to use the Microsoft Shop. The Microsoft Store provides installs of Python 3.vii, Python iii.eight, Python 3.9, and Python 3.10. Be aware that you might accept compatibility issues with some packages using this method.
For additional information about using Python on Windows, see Using Python on Windows at Python.org
macOS
The organisation install of Python on macOS is non supported. Instead, an installation through Homebrew is recommended. To install Python using Homebrew on macOS use brew install python3 at the Terminal prompt.
Notation On macOS, make sure the location of your VS Code installation is included in your PATH environment variable. See these setup instructions for more information.
Linux
The built-in Python 3 installation on Linux works well, simply to install other Python packages you must install pip with get-pip.py.
Other options
-
Information Scientific discipline: If your primary purpose for using Python is Data Science, and so you lot might consider a download from Anaconda. Anaconda provides not just a Python interpreter, but many useful libraries and tools for information science.
-
Windows Subsystem for Linux: If you are working on Windows and want a Linux environment for working with Python, the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is an option for you. If you choose this option, you lot'll also want to install the Remote - WSL extension. For more information about using WSL with VS Lawmaking, see VS Lawmaking Remote Development or try the Working in WSL tutorial, which will walk you through setting upward WSL, installing Python, and creating a Hi World application running in WSL.
Verify the Python installation
To verify that yous've installed Python successfully on your car, run i of the following commands (depending on your operating system):
-
Linux/macOS: open a Terminal Window and type the post-obit command:
python3 --version -
Windows: open a control prompt and run the following command:
py - three --version
If the installation was successful, the output window should show the version of Python that you installed.
Note You can employ the
py -0command in the VS Code integrated terminal to view the versions of python installed on your machine. The default interpreter is identified by an asterisk (*).
Get-go VS Code in a project (workspace) folder
Using a command prompt or terminal, create an empty folder called "hello", navigate into information technology, and open up VS Code (code) in that folder (.) by inbound the following commands:
mkdir hello cd hello code . Note: If y'all're using an Anaconda distribution, be sure to use an Anaconda command prompt.
By starting VS Lawmaking in a folder, that folder becomes your "workspace". VS Lawmaking stores settings that are specific to that workspace in .vscode/settings.json, which are split from user settings that are stored globally.
Alternately, you can run VS Lawmaking through the operating organization UI, then apply File > Open Folder to open up the project folder.
Select a Python interpreter
Python is an interpreted language, and in order to run Python code and get Python IntelliSense, you must tell VS Lawmaking which interpreter to use.
From within VS Code, select a Python 3 interpreter by opening the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)), start typing the Python: Select Interpreter control to search, so select the command. You lot tin also use the Select Python Environs choice on the Condition Bar if available (it may already show a selected interpreter, likewise):
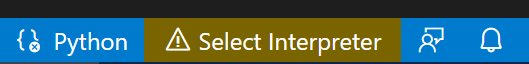
The command presents a listing of bachelor interpreters that VS Code tin discover automatically, including virtual environments. If you don't see the desired interpreter, see Configuring Python environments.
Note: When using an Anaconda distribution, the correct interpreter should have the suffix
('base':conda), for examplePython 3.seven.three 64-fleck ('base':conda).
Selecting an interpreter sets which interpreter volition be used by the Python extension for that workspace.
Note: If yous select an interpreter without a workspace folder open, VS Lawmaking sets
python.defaultInterpreterPathin User scope instead, which sets the default interpreter for VS Lawmaking in general. The user setting makes sure y'all always have a default interpreter for Python projects. The workspace settings lets you override the user setting.
Create a Python Hello World source lawmaking file
From the File Explorer toolbar, select the New File push button on the hello folder:
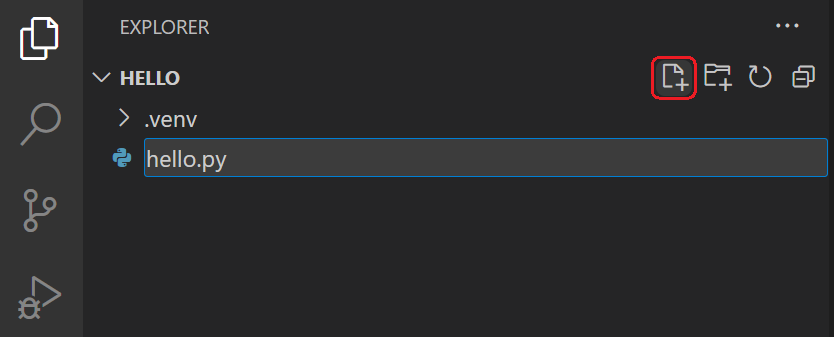
Name the file howdy.py, and it automatically opens in the editor:
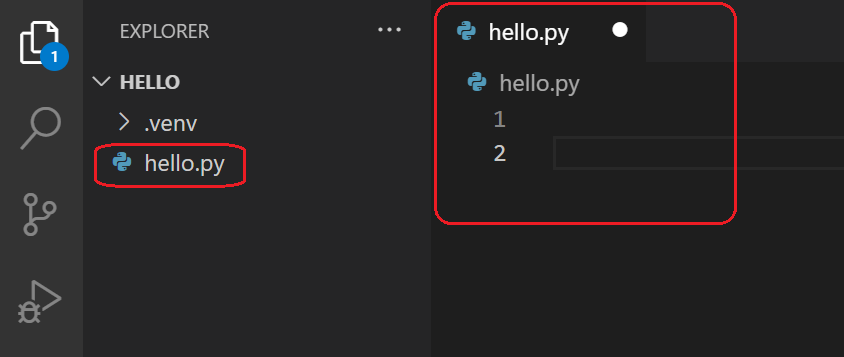
By using the .py file extension, you tell VS Lawmaking to interpret this file as a Python program, so that information technology evaluates the contents with the Python extension and the selected interpreter.
Note: The File Explorer toolbar also allows you to create folders within your workspace to ameliorate organize your code. Y'all can utilise the New binder button to chop-chop create a folder.
Now that you have a code file in your Workspace, enter the following source code in howdy.py:
msg = "How-do-you-do Globe" impress (msg) When y'all start typing print, notice how IntelliSense presents motorcar-completion options.
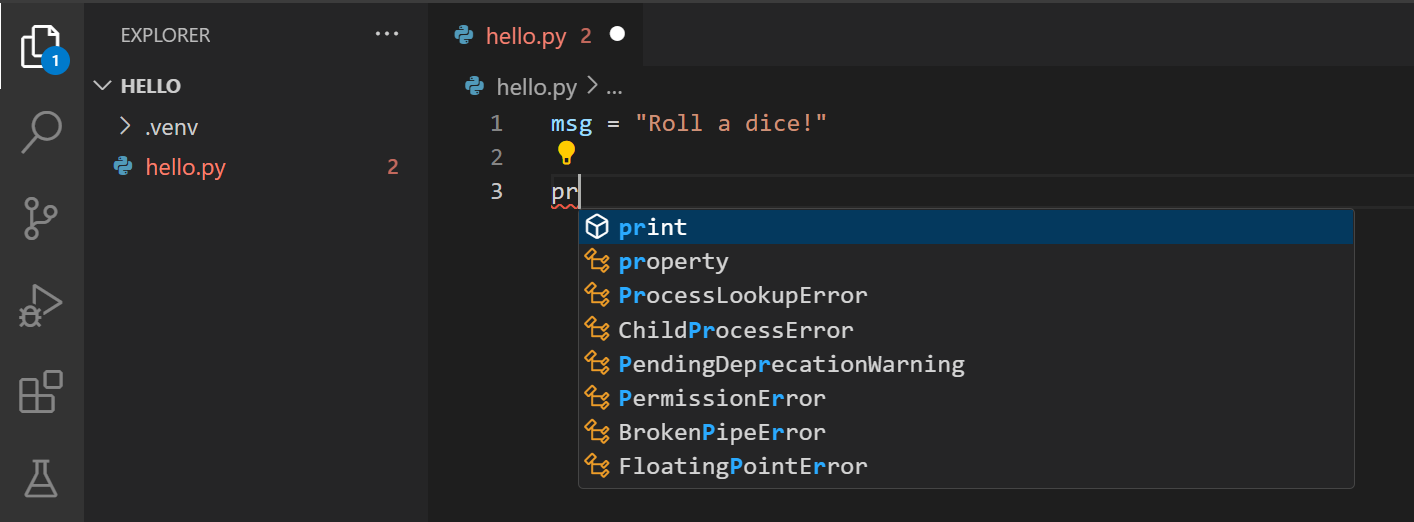
IntelliSense and auto-completions work for standard Python modules every bit well as other packages you've installed into the environs of the selected Python interpreter. It also provides completions for methods bachelor on object types. For case, because the msg variable contains a string, IntelliSense provides string methods when y'all type msg.:
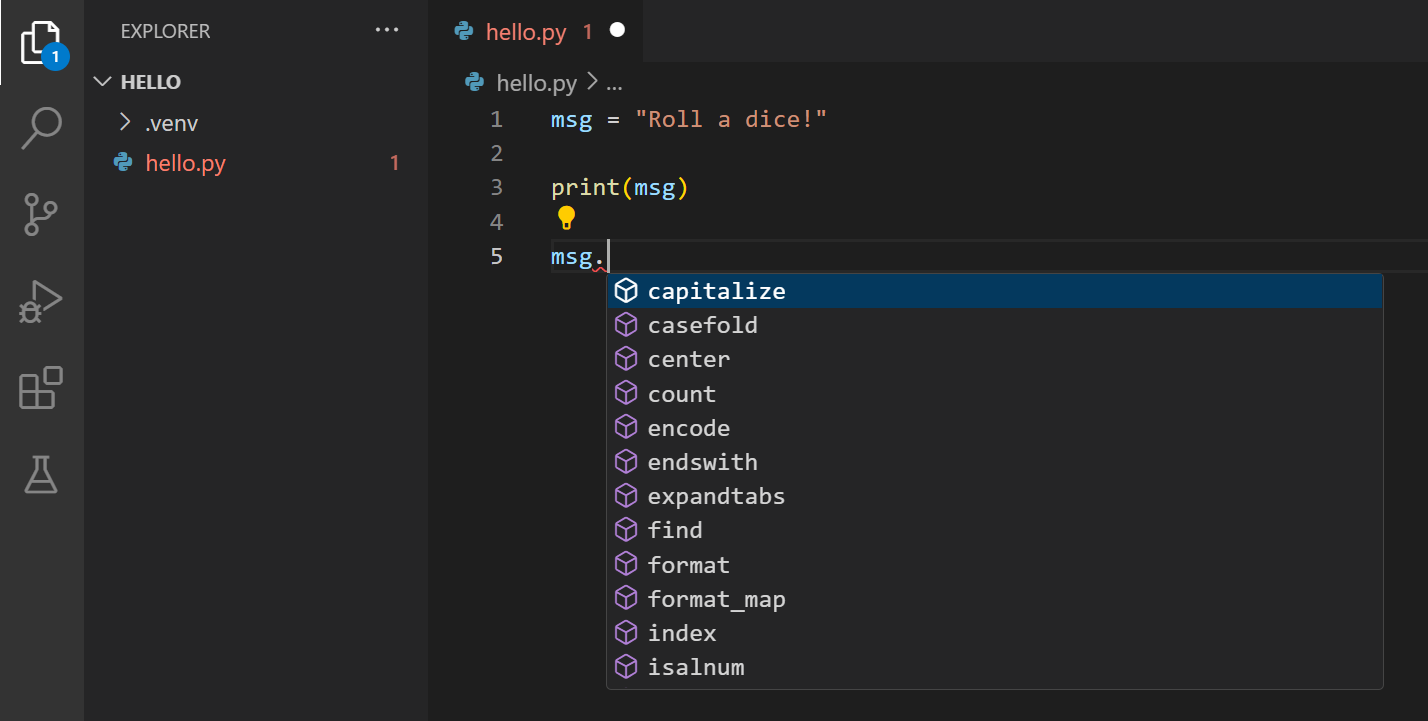
Feel gratuitous to experiment with IntelliSense some more than, but so revert your changes and then you have simply the msg variable and the print call, and salve the file ( ⌘South (Windows, Linux Ctrl+S)).
For full details on editing, formatting, and refactoring, see Editing lawmaking. The Python extension also has full back up for Linting.
Run Hello Globe
It'south simple to run hello.py with Python. Just click the Run Python File in Final play button in the top-right side of the editor.
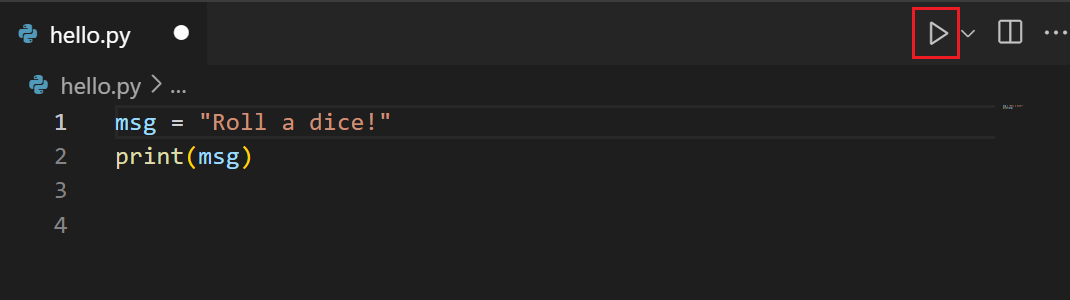
The button opens a terminal panel in which your Python interpreter is automatically activated, then runs python3 hello.py (macOS/Linux) or python how-do-you-do.py (Windows):
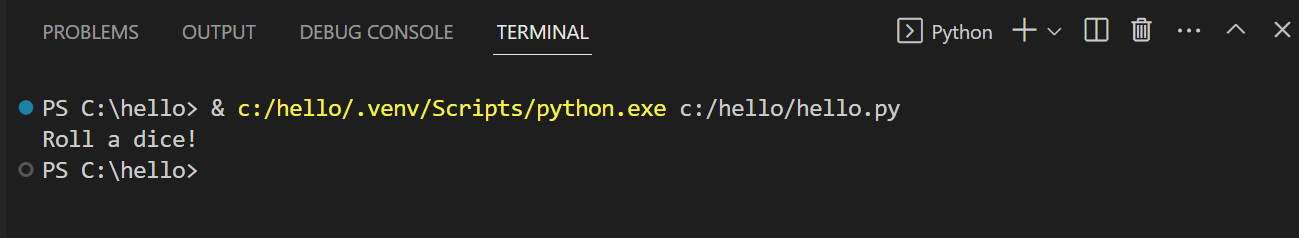
In that location are three other ways yous can run Python code inside VS Code:
-
Right-click anywhere in the editor window and select Run Python File in Final (which saves the file automatically):
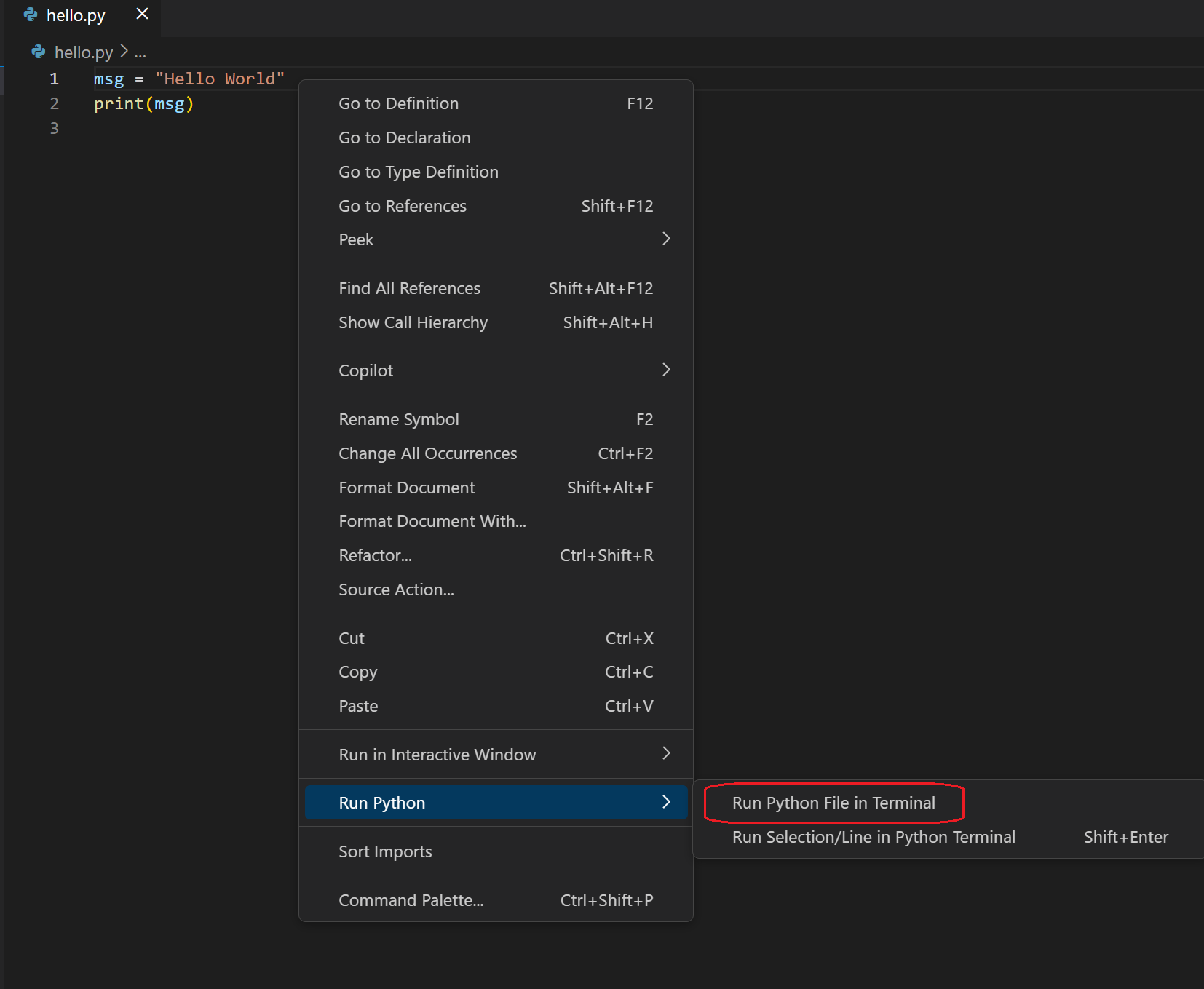
-
Select one or more lines, then press Shift+Enter or right-click and select Run Pick/Line in Python Terminal. This command is user-friendly for testing merely a part of a file.
-
From the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)), select the Python: Start REPL command to open a REPL concluding for the currently selected Python interpreter. In the REPL, y'all can then enter and run lines of code one at a time.
Configure and run the debugger
Let's at present endeavor debugging our simple How-do-you-do World program.
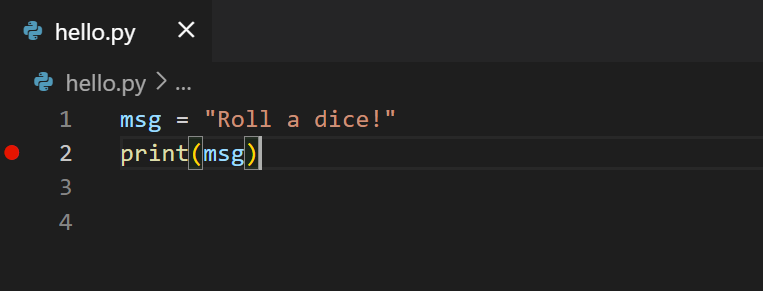
First, ready a breakpoint on line 2 of hello.py by placing the cursor on the impress call and pressing F9 . Alternately, just click in the editor's left gutter, side by side to the line numbers. When you set a breakpoint, a red circle appears in the gutter.
Adjacent, to initialize the debugger, press F5 . Since this is your outset fourth dimension debugging this file, a configuration menu volition open from the Command Palette assuasive you to select the type of debug configuration you would like for the opened file.

Annotation: VS Code uses JSON files for all of its various configurations; launch.json is the standard name for a file containing debugging configurations.
These dissimilar configurations are fully explained in Debugging configurations; for now, just select Python File, which is the configuration that runs the current file shown in the editor using the currently selected Python interpreter.
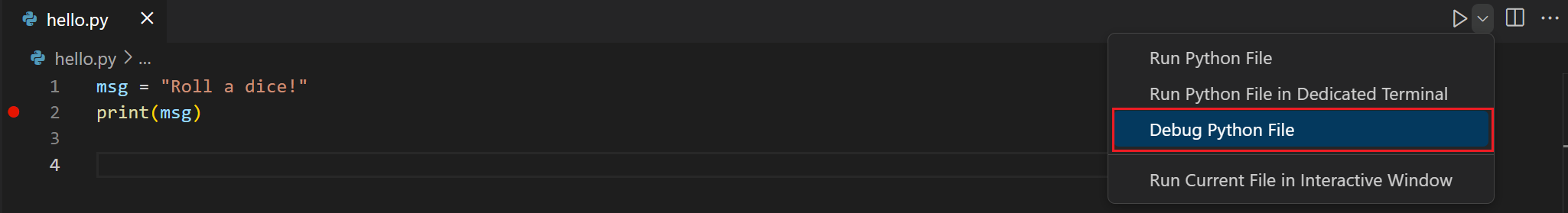
You can also start the debugger by clicking on the down-pointer next to the run push on the editor, and selecting Debug Python File in Terminal.
The debugger will stop at the start line of the file breakpoint. The current line is indicated with a yellow arrow in the left margin. If you lot examine the Local variables window at this point, you lot will see at present defined msg variable appears in the Local pane.
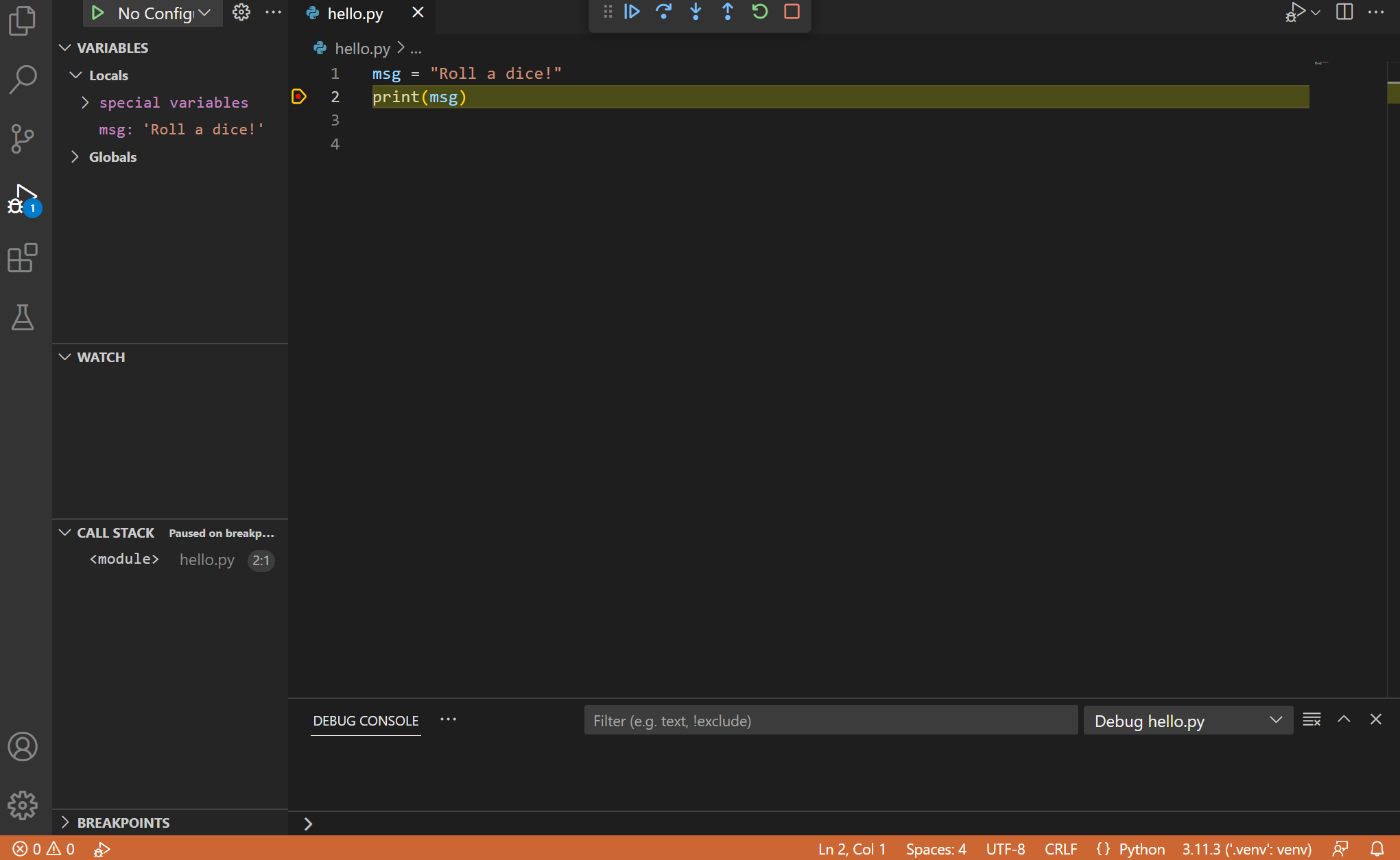
A debug toolbar appears along the elevation with the following commands from left to right: go along ( F5 ), step over ( F10 ), stride into ( F11 ), step out ( ⇧F11 (Windows, Linux Shift+F11)), restart ( ⇧⌘F5 (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+F5)), and cease ( ⇧F5 (Windows, Linux Shift+F5)).
The Status Bar too changes color (orange in many themes) to indicate that you lot're in debug way. The Python Debug Console also appears automatically in the lower right panel to evidence the commands being run, along with the program output.
To continue running the programme, select the keep control on the debug toolbar ( F5 ). The debugger runs the program to the terminate.
Tip Debugging data tin as well be seen by hovering over lawmaking, such as variables. In the case of
msg, hovering over the variable volition brandish the cordHi worldin a box above the variable.
You tin can also work with variables in the Debug Console (If you don't see information technology, select Debug Console in the lower correct area of VS Code, or select it from the ... bill of fare.) Then try entering the following lines, one past 1, at the > prompt at the bottom of the console:
msg msg.capitalize() msg.carve up() 
Select the blue Continue button on the toolbar over again (or press F5) to run the program to completion. "Hello Earth" appears in the Python Debug Console if you switch back to it, and VS Code exits debugging mode once the programme is complete.
If yous restart the debugger, the debugger again stops on the outset breakpoint.
To end running a program earlier it'south complete, use the red square stop button on the debug toolbar ( ⇧F5 (Windows, Linux Shift+F5)), or apply the Run > Stop debugging menu control.
For full details, see Debugging configurations, which includes notes on how to use a specific Python interpreter for debugging.
Tip: Use Logpoints instead of print statements: Developers often litter source code with
impressstatements to quickly inspect variables without necessarily stepping through each line of code in a debugger. In VS Lawmaking, yous can instead use Logpoints. A Logpoint is like a breakpoint except that it logs a message to the console and doesn't stop the program. For more than information, meet Logpoints in the main VS Code debugging article.
Install and utilise packages
Let's now run an instance that's a piddling more interesting. In Python, packages are how you obtain whatever number of useful code libraries, typically from PyPI. For this example, you utilise the matplotlib and numpy packages to create a graphical plot as is normally washed with information science. (Annotation that matplotlib cannot prove graphs when running in the Windows Subsystem for Linux as it lacks the necessary UI support.)
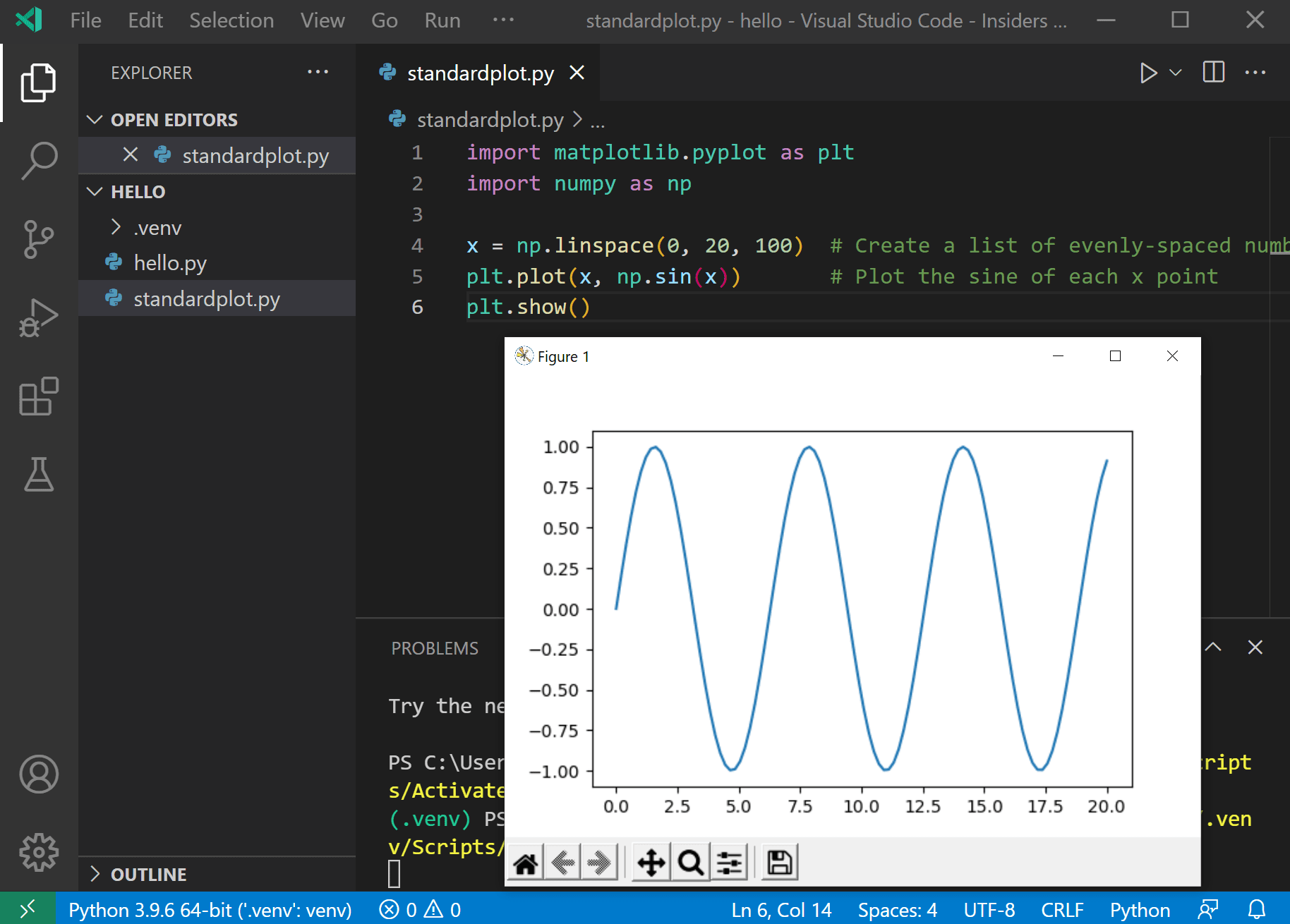
Return to the Explorer view (the peak-nearly icon on the left side, which shows files), create a new file chosen standardplot.py, and paste in the following source lawmaking:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np 10 = np.linspace( 0 , xx , 100 ) # Create a list of evenly-spaced numbers over the range plt.plot(ten, np.sin(10)) # Plot the sine of each x point plt.show() # Display the plot Tip: If you enter the above lawmaking by hand, you lot may observe that auto-completions change the names after the
askeywords when you press Enter at the terminate of a line. To avoid this, type a space, then Enter.
Next, try running the file in the debugger using the "Python: Current file" configuration as described in the last section.
Unless y'all're using an Anaconda distribution or take previously installed the matplotlib parcel, you should run into the message, "ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'matplotlib'". Such a bulletin indicates that the required package isn't available in your organisation.
To install the matplotlib package (which as well installs numpy every bit a dependency), end the debugger and use the Control Palette to run Concluding: Create New Terminal ( ⌃⇧` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+`)). This command opens a command prompt for your selected interpreter.
A best do amongst Python developers is to avoid installing packages into a global interpreter environment. You instead use a project-specific virtual surround that contains a copy of a global interpreter. Once y'all activate that surround, any packages you then install are isolated from other environments. Such isolation reduces many complications that tin arise from conflicting package versions. To create a virtual environs and install the required packages, enter the following commands equally appropriate for your operating system:
Note: For additional information about virtual environments, come across Environments.
-
Create and actuate the virtual surroundings
Annotation: When you create a new virtual environment, yous should be prompted by VS Lawmaking to set it as the default for your workspace folder. If selected, the environment volition automatically be activated when yous open a new terminal.

For Windows
py -3 - m venv .venv . venv \ scripts \ activateIf the actuate command generates the message "Activate.ps1 is non digitally signed. You cannot run this script on the electric current organisation.", and so y'all need to temporarily change the PowerShell execution policy to let scripts to run (see Near Execution Policies in the PowerShell documentation):
Set - ExecutionPolicy - ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned - Scope ProcessFor macOS/Linux
python3 -one thousand venv .venv source .venv/bin/actuate -
Select your new environment past using the Python: Select Interpreter control from the Control Palette.
-
Install the packages
# Don't use with Anaconda distributions because they include matplotlib already. # macOS python3 -m pip install matplotlib # Windows (may crave elevation) python -thousand pip install matplotlib # Linux (Debian) apt-get install python3-tk python3 -m pip install matplotlib -
Rerun the program now (with or without the debugger) and later on a few moments a plot window appears with the output:
-
In one case yous are finished, type
deactivatein the last window to deactivate the virtual environment.
For boosted examples of creating and activating a virtual environment and installing packages, meet the Django tutorial and the Flask tutorial.
Side by side steps
Y'all can configure VS Code to utilise whatsoever Python surroundings you have installed, including virtual and conda environments. You can also utilise a divide environment for debugging. For full details, meet Environments.
To learn more almost the Python linguistic communication, follow any of the programming tutorials listed on python.org within the context of VS Code.
To learn to build web apps with the Django and Flask frameworks, encounter the following tutorials:
- Employ Django in Visual Studio Code
- Utilize Flask in Visual Studio Code
At that place is then much more to explore with Python in Visual Studio Code:
- Editing code - Learn about autocomplete, IntelliSense, formatting, and refactoring for Python.
- Linting - Enable, configure, and apply a diverseness of Python linters.
- Debugging - Learn to debug Python both locally and remotely.
- Testing - Configure test environments and discover, run, and debug tests.
- Settings reference - Explore the full range of Python-related settings in VS Code.
- Deploy Python to Azure App Service using containers
- Deploy Python to Azure App Service on Linux
Source: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/python-tutorial
Posted by: ransdellnotle1998.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Run A Python Script In Windows Terminal"
Post a Comment